Sewing threads are the basis for creating seams and joining fabrics during the sewing process. They are thin fibers twisted into a thread. Depending on the composition, thickness and other characteristics, they can be used for different types of fabrics and seams.
Viewby material
For convenience and standardization, manufacturers use a letter code to mark their threads. It consists of 1 or more letters, each of which denotes a certain parameter of the thread: the letter "L" denotes polyester, the letter "K" denotes nylon, and the letter "LSh" denotes polyester.
The letter code is not a universal standard and may vary depending on the manufacturer.
Natural
Sewing threads can be made from natural fibers.

| Material | Brief description |
| Cotton | Sewing threads made of cotton fibers are in great demand due to their unique properties. They are hypoallergenic and highly absorbent. They are durable and elastic. These threads retain color well and do not fade under the influence of sunlight, but their disadvantage is their tendency to shrink when washed. |
| Marsherized (cotton) | Marsherization is the treatment of cotton fibers with an alkali solution, which gives them additional shine and softness. Marsherized threads have increased strength compared to regular cotton threads and are less susceptible to shrinkage. Their shiny surface makes stitches neat and beautiful to look at. These threads are often used for decorative finishing work. |
| Wool | Wool sewing threads are made from sheep's wool fibers and are great for working with warm winter clothing. They are elastic, soft to the touch, and have excellent thermal insulation. The downside is that they can cause irritation to people with sensitive skin. |
| Bamboo | Bamboo fiber threads have an antibacterial effect, keep you cool in summer and warm in winter. They are hypoallergenic, soft and durable, making them suitable for creating a variety of clothing. |
| Silk | Silk sewing threads are soft and have a natural shine. They are used to create high-quality clothing and intimate accessories. Silk threads are very strong despite their thinness, are resistant to decay and provide a smooth passage through any fabric without damage. |
| Flax | Linen sewing threads are valued for their strength and durability. They do not stretch over time like cotton or silk analogs. Linen also has a natural shine and antibacterial properties, which makes it an excellent choice for sewing summer items: scarves, tablecloths or decorative interior elements. |
In addition to these basic materials, there are others, such as hemp, jute. But they are very rare and are intended for narrow tasks.
Artificial
In modern production of sewing threads, artificial fibers such as viscose are widely used.

| Material | Brief description |
| Viscose | Viscose is an artificial fiber made from cellulose. Due to its unique structure, it has a number of advantages: softness, flexibility and shape stability. Viscose threads are widely used for both sewing clothes and creating home textiles. |
Synthetic
Synthetic materials, due to their diversity, provide the opportunity for an optimal choice for any task in sewing production.
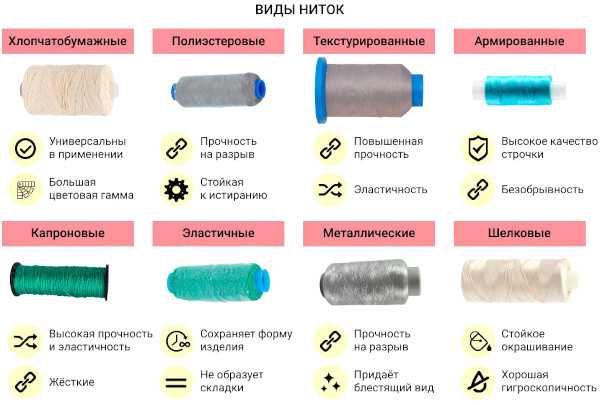
| Name of material | Brief description |
| Nylon | Nylon threads are one of the earliest synthetic fibers. They are highly wear-resistant and tear-resistant. Nylon does not absorb moisture and dries quickly, making it an excellent choice for activewear, swimsuits, and sports equipment. The disadvantage of nylon threads may be their tendency to melt at high temperatures and lower resistance to ultraviolet radiation compared to other materials. |
| Polyester | Polyester sewing threads are resistant to most chemicals, do not change color when exposed to UV light, and do not absorb odors, making them a great choice for everyday clothing. Polyester is well suited for machine sewing because it is less likely to loop or twist. |
| Acrylic | Acrylic threads are often used to make textiles such as warm sweaters or plush toys because of their thermal insulation properties. They are soft to the touch and come in a wide range of colors. Although acrylic is less durable than other types of synthetic fibers, it retains its shape well and is hypoallergenic. |
| Lavsan | Lavsan is polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Lavsan sewing threads are characterized by high strength, resistance to wear and chemicals. They are most often used in the production of workwear, canvas. |
| Polyamide | Polyamide threads have proven themselves as strong, wear-resistant materials with the ability to quickly restore shape after deformation. This makes polyamide material preferable for the production of, for example, functional underwear or compression products. |
| Nylon | Capron is a type of polyamide with a specific macromolecule structure. Capron sewing threads are distinguished by increased resistance to friction and chemical stability. They are used to produce rigid elements of clothing or, for example, covers. |
Mixed
Threads, the types of which allow designers to create unique clothing, can be mixed. This is a type of thread that is obtained by combining fibers of different origins. They can include both natural and synthetic components.
The main goal of creating mixed threads is to combine the best qualities of different materials to achieve optimal performance properties.

Blended sewing threads may include a combination of fibers:
- polyester/cotton: have good strength and wear resistance;
- silk/polyamide: shiny and durable threads for decorative finishing;
- Viscose/Lycra: elastic threads for knitwear.
Mixed sewing threads are used in almost all areas of light industry:
- when sewing clothes to reinforce seams on items made from stretch fabrics or to treat business suits;
- in the textile industry for the production of bed linen or furniture upholstery;
- in the production of workwear, where additional strength and wear resistance of materials is required.
Advantages:
- versatility (suitable for most types of fabrics);
- strength (withstand high tensile loads);
- elasticity (prevents stretching or compression of the seam);
- wear resistance (extend the service life of products);
- cost (often mixed threads are more economical than purely natural ones).

Flaws:
- possible instability of quality when using components of different origins;
- less environmentally friendly, especially if it contains synthetic components;
- risk of allergic reactions in end users to certain types of fibres;
- Some types of blended threads may be less suitable for dyeing;
By finishing method
Depending on the finishing method, sewing threads can have different appearance and properties.
With a shiny surface
Usually made from synthetic fibers. They have a smooth and shiny surface, which gives the product an elegant and stylish look. These threads are used for sewing elegant clothes, such as evening and wedding dresses.
Matte classic
Made from natural or synthetic fibers, these threads are used to sew everyday clothing such as jeans, T-shirts, and other items.
Rough, not bleached or cleaned
Threads with natural color and texture. Used for sewing items from coarse and dense fabrics, such as denim, canvas, and others. They provide a strong connection of parts and do not break when stretched.
Colored
The threads, the types of which are described in this article, have different colors and shades.
They are used to create decorative elements on clothing, such as:
- embroidery;
- applique;
- finishing and others.
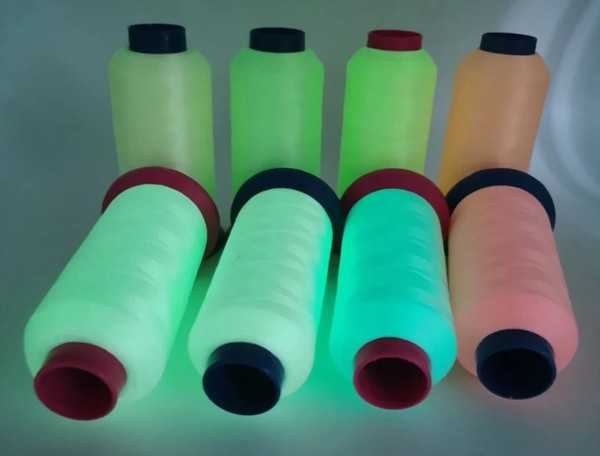

Colored threads allow you to create bright and colorful products that attract attention and evoke positive emotions.
| Name of the species | Brief description |
| Melange threads | Includes fibers of different colors. They are used to create a 3D effect. Melange threads can be used for sewing products from any fabric. |
| Chameleons | This is a type of thread that changes color depending on the viewing angle. It is used for decorative purposes. |
Special
Special threads ensure reliable connection of parts and durability of products.

| Type of thread | Brief description |
| Moisture resistant | They are used for sewing items that will be exposed to moisture, such as outerwear or footwear. They are made from special materials that do not absorb water and do not lose their properties when wet. |
| Fire resistant | Used for sewing items that must meet fire safety requirements. They are made from materials that do not support combustion and do not emit toxic substances when heated. |
| Flavored | They are used to give products a pleasant smell. They can be impregnated with various aromatic substances, such as essential oils. |
| Reflective | Contains a special material that reflects light. Such threads are used to increase visibility in the dark, which is especially important for special clothing, such as the uniform of road service workers or security personnel. |
| Metallized | They have a shiny surface that resembles a metallic sheen. They can be made of various materials, such as aluminum, copper or other metals and their alloys. They are widely used in the production of fashionable clothes. |
| Fluorescent | They contain a special luminescent material that absorbs light and then emits it in the dark. Luminescent threads are used in the production of clothing and accessories to create unusual and bright effects. |
By structure
Depending on the structure, sewing threads can be divided into several types.
General purpose
This is the most common type of sewing thread. It is used for sewing most items made from medium-weight fabrics. General-purpose threads are made from natural or synthetic fibers.
Twist
This is a type of thread with a twisted structure. They are used for sewing items from thin fabrics, such as silk or chiffon. Twist provides strength and elasticity to the seam.
Monofilament
This is a thin thread made from synthetic materials such as polyester, polyamide or polypropylene. It has a smooth surface and high tensile strength. Monofilament is used for machine seams, overcasting edges and making decorative elements.
Water soluble
These are threads that dissolve in water at a certain temperature. They are made from natural or synthetic fibers that are treated with a special composition.

Water-soluble threads are used for temporary joining of parts, for example, when sewing corsets, swimsuits and other items that require subsequent processing.
Textured
Threads, the types of which allow sewing elegant things, can be textured. This is a material with a voluminous or relief surface. They can be made of 100% polyester. Textured threads are used to create decorative seams, underwear.
Threads for assembly
These are thin polyester threads that are used for adjustment when ironing. They are made from synthetic fibers.
Assembly threads are used to create:
- darts;
- folds;
- assemblies;
- embroidery.
Elastic thread
This is a highly elastic thread used to create elastic seams and finishes. It is made from synthetic fibers such as latex or polyurethane and has different types of weave.

Elastic thread is used to make:
- cuff;
- collars;
- belts;
- other items of clothing and footwear that should fit snugly to the body.
Reinforced
This is a type of thread that is used for sewing items made of heavy fabrics such as leather, denim and others. They have increased strength and abrasion resistance, which makes them ideal for use in the production of workwear, footwear and other products that require high seam strength.
High-strength threads
This is another type of thread designed for sewing items that require increased seam strength. They are used for dense fabrics such as tarpaulin, canvas, and others. High-strength threads can also be used for sewing items that are exposed to moisture or other adverse conditions.
Embroidery
This is a type of thread designed for embroidering various patterns on fabric. They are thin with numerous shades.

Embroidery threads can be used to create decorative elements on:
- clothes;
- bed linen;
- tablecloths and other products.
Shoe sewing threads
These threads are usually made of polyester or nylon, which makes them durable and resistant to stretching. They also have a high degree of elasticity, not breaking under increased loads.
Available in a variety of thicknesses and colors, they are widely used to create strong, durable seams that can withstand long-term use and heavy use.
By thickness
Threads, the types of which differ in thickness, can be thick and thin. Thickness affects the strength and durability of the seam, as well as the appearance of the product.
Threads can be divided into several types according to this parameter:
| Name | Thickness, text | Brief description |
| Thin | from 60 to 110 | Used for working with thin fabrics such as:
They provide a neat and invisible seam. |
| Average | from 20 to 60 | Suitable for use with most fabrics including:
They ensure the strength and durability of the seam. |
| Fat | from 15 to 20 | Used for working with dense fabrics such as:
They provide reliable connection of parts and strengthening of seams. |
Sewing thread markings may vary depending on the manufacturer.
One common method is to use numerical values. For example, the thickness of a thread can be indicated by numbers from 8 to 120. The smaller the number, the thinner the sewing silk thread. The opposite is true for cotton threads.
For thin fabrics, it is recommended to use thin cotton threads with a small numerical value of thickness No. 70, 80. For cotton and linen, thick wool, corduroy, denim, it is recommended to use threads with a larger numerical value of thickness No. 40. And No. 20, 30 are used for leather.

The second way to indicate thickness is to use letter values. In this case, the letter A denotes the thinnest thread, and the letter G – the thickest. In addition to the alphabetical values, there are additional subclasses, such as “00” or “000”, which indicate thinner versions of threads.
By appointment
Threads are used to connect parts, giving strength and an aesthetic appearance to finished products.
For overlock
They are designed for use on an overlock machine, which provides professional finishing of fabric edges. They are thinner, but strong and elastic. There are different types, but most often polyester, viscose and nylon.
Elastic
Used to create elastic seams that can stretch and return to their original position. They are used when sewing clothes from elastic fabrics such as lycra or spandex.
For sewing machine
These threads are designed for use on various types of sewing machines. They are highly durable and abrasion resistant. They can be cotton, viscose or polyester.
For the top line
These polyester threads are used to topstitch fabric. They must be strong, abrasion resistant and have an attractive appearance.
Bobbin
Used in shuttle sewing machines, they are thinner and lighter than those for the top stitch to ensure proper operation of the mechanism.
Basting
Used to temporarily connect parts before the main stitching. They have low strength and are easily removed after finishing the work.
By the number of additions
One of the important aspects of choosing a thread is the number of strands it has.
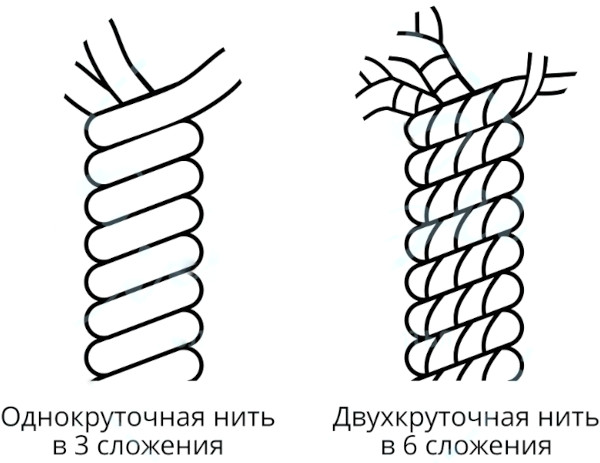
| Number of twists | Number of additions | Brief description |
| 1-twist threads | with 2 or 3 | These are the most common types of threads. They are strong and resistant to stretching, making them ideal for most types of sewing work. |
| 2-twist threads | from 4, 6, 9 or 12 | They are even more durable and resistant. They are used in more demanding projects, such as leather goods or as decorative elements. Their unique structure provides stronger and more durable seams. |
By twist coefficient and its direction
The twist of the thread can be right (Z) or left (S), which is determined by the direction of the turns around the axis of the thread.
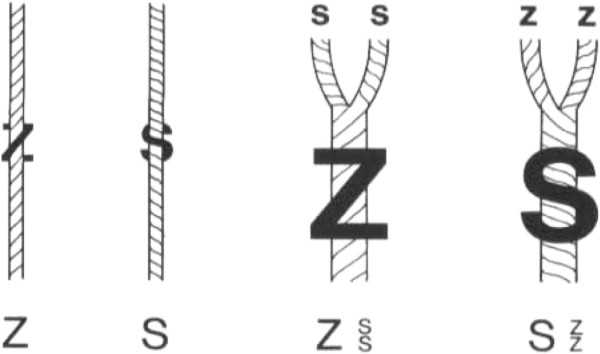
To determine the twist coefficient of a thread, you can use several methods:
| Way | Description |
| in visual analysis | You need to examine the pile of the thread under a magnifying glass. If it has the form of a spiral, the turns of which go to the right, then the thread has a right twist. If the turns go to the left, then the thread has a left twist. Then you can compare the visual sample with others with a known twist coefficient to determine it approximately for the threads under study. |
| thread twist test | Fix one end of the thread and rotate the other around its axis. If the thread turns counterclockwise when twisting, the thread has a right twist. If the turns go clockwise, the thread has a left twist. You can make several turns and determine how much the thread is twisted to roughly determine the twist coefficient. |
Sewing threads are textiles used to join together clothing and other items. They provide strength and durability to seams and determine the appearance of the finished product.
The choice of sewing threads depends on the requirements for strength, elasticity, moisture resistance and other characteristics that are necessary for a particular product.
Video about sewing threads
How to choose threads for sewing:
