In crocheting, there are 2 main techniques for making loops: double crochets and single crochets. They also have several varieties. Depending on the type of loop, different patterns are obtained on the knitted fabric. Sometimes, to create a pattern, you need to combine several types of loops. Therefore, to crochet, you need to know not only the algorithm for performing basic elements, but also additional techniques for knitting loops.
Types of columns in crochet, designation in diagrams
The double crochet and the single crochet are knitted using uniform patterns. Having mastered the basic elements, you will be able to knit any pattern using graphic patterns.
Types of columns:
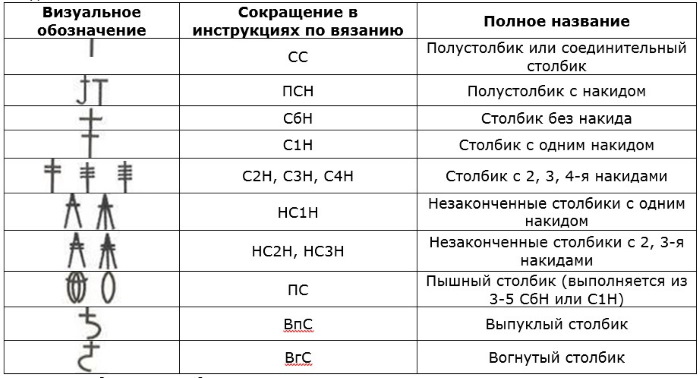
In addition to columns, the basic elements used in knitting include the air loop (AL), which is depicted in diagrams as an uncolored circle.
Instructions for knitting a single crochet stitch
The single crochet stitch is a basic element of crochet. It is used in almost all products, often being its basis. The finished fabric, knitted from sbN, looks dense, almost does not stretch. The technique of performing all types of columns (St) is based on this knitting element.
At the top of the column, a loop is formed in which the front (closer to the knitter) and back walls are distinguished.
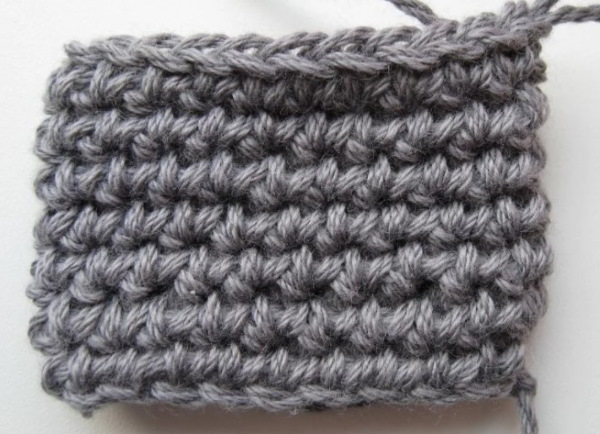

There are 3 ways to perform sc behind the loop walls:
- for the front;
- behind;
- for 2 at once.
Depending on the technique of performing the sc, the appearance, density, elasticity and thickness of the fabric will differ. To get a smooth surface, you need to perform the sc for 2 walls. To get a protruding line on the front side of the product, the thread is grabbed by the front wall. The recessed connection of the rows comes out when the thread is grabbed by the back wall.
Attention! When analyzing schematic instructions for making patterns, when no other condition is specified, it is customary to make loops for 2 walls.
Algorithm for knitting sc:
- Perform 10-15 air loops (AL) and 1 lifting loop (LL) to move to the 2nd row.
- Place the tool behind 2 walls of the 1st P in the row, pick up the working thread.
- Pull the thread through the loop so that you have 2 sts on the tool.
- Once again, pick up the working thread with the hook and pull it through 2 P.
On the hook after performing Sc there remains 1 working loop. Then the whole row is performed in the same way. To get an even and beautiful end edge, you need to correctly perform the first and last loop.

Beginner needlewomen often do not see the beginning and end of knitting, so they skip loops. To prevent the fabric from slipping to the side, you need to count the loops all the time. If at some point one is missing, the row will have to be unraveled and knitted again, starting with the first loop.
Single crochet stitches for the front and back wall
If you need to highlight the place where the rows are connected with a horizontal convex or concave line, make the posts behind the front or back wall of the loops. Note: the first loop of the row is always knitted behind 2 walls, which helps to maintain the density and shape of the knitted fabric.
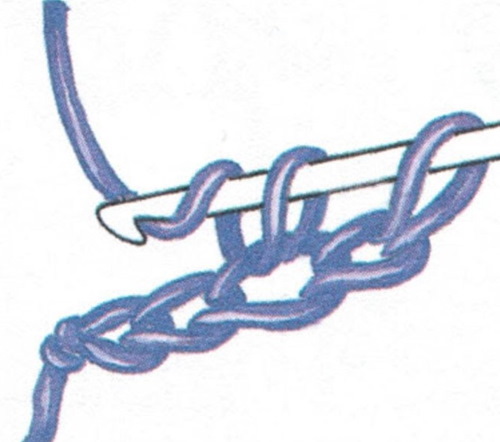
The algorithm for knitting loops is identical to performing columns for both walls. The result will differ visually.

In the lower part of the fabric, the loops are knitted behind the front wall, in the upper part – behind the back wall.
Methods of knitting a single crochet stitch with a difference in appearance
Single crochet stitches can be done in different ways, depending on this the appearance of the fabric, its density, and volume will change.
Neat columns
This method will allow you to knit clear columns that look like cross stitch:
- Cast on a chain of VP and close into a circle using SS.
- Insert the hook behind 2 walls of the next loop.
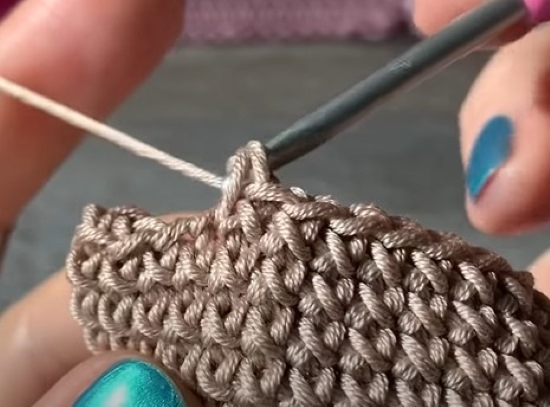





- The working thread is tied at the top (thanks to the top tie, the thread St is twisted in the right way to form a cross).
- Pull through 2 walls.
- Knit 2 sts together, catching the working thread from below.
The method is suitable for knitting in a circle, making bags, backpacks, slippers.
Double sided single crochet
This method can be used for knitting in a circle and in turning rows. The pattern will be the same and neat on both sides. This is one of the densest patterns in crocheting. It is suitable for making rugs, table coasters. The fabric holds its shape well, so you won’t be able to make a bedspread or clothes with this pattern.
 Knitting algorithm:
Knitting algorithm:
- To raise between rows, make 1 VP.
- The first row is knitted with simple sc.
- On the next row, insert the hook under 2 strips of the loop and between its side walls.
- Grab the working thread from above, pull it out of the loop and knit a regular sc.
- Continue knitting in the same way until the end of the row.

When making a pattern, do not tighten the loops too tightly. You can use a hook 0.5-1 number larger than the thickness of the yarn.
Braided posts (method #1)
The pattern is suitable for knitting dense items - bags, baskets, covers, etc. It is knitted in a circle, it turns out to be slightly elastic, so the finished products do not stretch and retain a neat appearance for a long time. If you choose acrylic or other synthetic yarn, the fabric will not deform after washing.
The advantage of this knitting technique is the double-sided pattern, which looks equally beautiful on the front and back sides.
Face:

Back side of the pattern:

Instructions for making braided loops:
- Close the ring from VP.
- 1 Row is knitted with regular sc, as in the cross pattern.
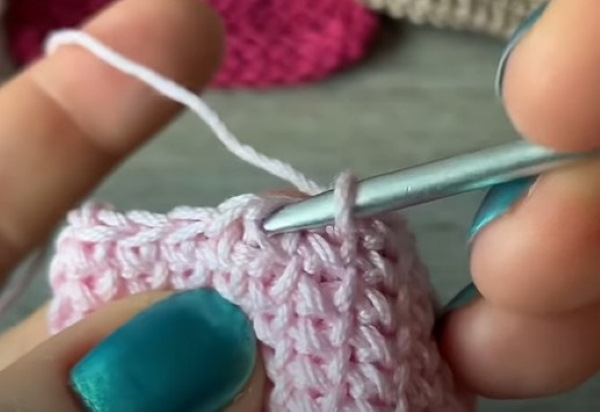

- On the next round, insert the tool into the center of the next loop.
- Grab the working thread and knit a single crochet stitch in the shape of a cross.
The pattern is different due to the fact that the working thread is brought out not through the 2 walls of the loop, but through the middle of the column from the bottom row.
Braided posts (method #2)
This pattern is knitted in a circle. The rows are lower than when knitting regular sc. The fabric is more elastic.

Knitting algorithm:
- Make a chain of VP, close it into a circle.
- 1 Row knit with regular sc.
- Insert the hook under the first strip P of the bottom row.
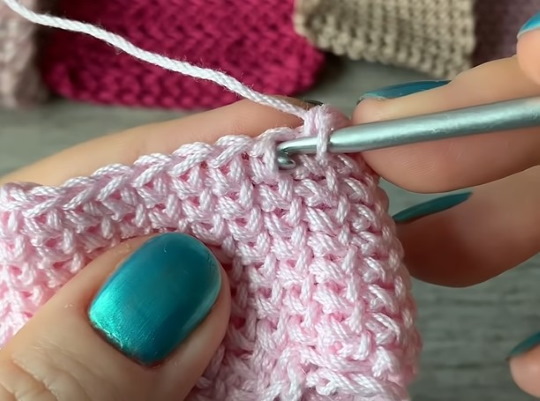

- Catch the working thread with the upper grip.
- Perform SBN.
- Repeat with all loops in the row.

- In the 1st P of the next row, insert the hook behind the back wall and at the same time inside the loop from the wrong side.
- Pick up the working thread from above and knit a single crochet.
- Continue knitting all the stitches in the row in the same way.

- The following rows are worked using the alternating method, first knitting the pattern as in Row 1, and then as in Row 2.
Single crochet stitches with a knot
The pattern can be knitted in 2 ways: rotary (photo 1) and circular (photo 2). The fabric knitted in a circle is denser and does not stretch well. To make the pattern neat, the hook size should match the thickness of the yarn. If you take a hook larger than the diameter of the thread, you can knit an openwork cardigan or a summer T-shirt that will be translucent.
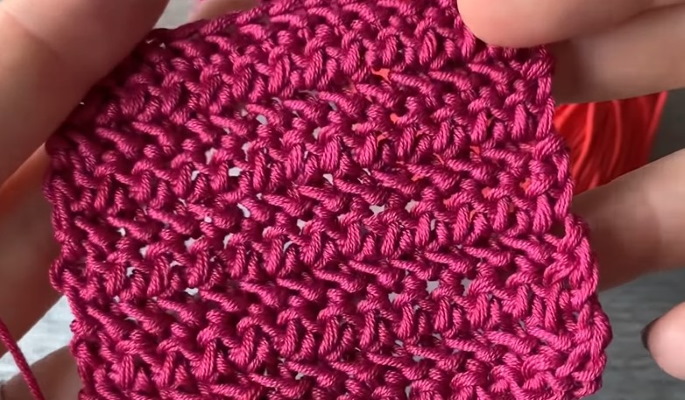


Algorithm for making a pattern:
- Cast on a chain of VP + 2 lifting VP.
- From the inside, yarn over the hook to form a knot.

- Insert the hook behind 2 walls of the P of the bottom row.

- Grab the thread from above, pull it through the bottom P and pull it through the yarn over.

- 2 P on the instrument perform together as a regular Sc.

- The sequence of actions is repeated until the end of the row.
The pearl effect pattern is both dense and elastic.
Connecting column (half column)
Half-columns (CC) are the lowest of all. The fabric knitted from them is tight, dense, and almost does not stretch. Slip stitches are rarely used as the main element in knitting products. They are usually used to tie the edge of the fabric or connect parts. Half-columns are also convenient for knitting (like embroidery) a pattern on a finished fabric.
It is inconvenient and difficult to start knitting half-columns immediately after a chain of air loops (VP), especially for people who are doing it for the first time. Therefore, they start working with a set of VP, then knit 1 row as Sc, and then knit half-columns. At the beginning of the row, the lifting loop is not made.
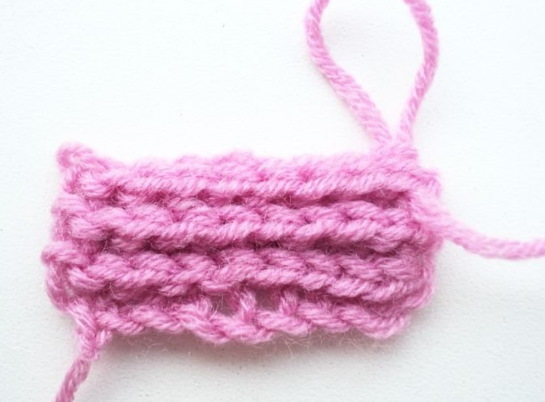

Knitting algorithm:
- The tool is inserted into the 1st P of the new row behind 2 walls.
- They grab the working thread.
- Pull the thread straight through the P on the hook.

It turns out that the slip stitch is the fastest and easiest to knit. But because of its small height, creating a large canvas only from SS loops will take twice as much time as when knitting ScN.

Advice: when knitting half-columns, do not pull the thread too tightly. The loops are not elastic, so the fabric will narrow and lose its shape as you add rows.
Columns with 1, 2, 3 and more yarn overs
The double crochet and the single crochet are crocheted according to the same pattern. The difference in the first option is only in the presence of an additional loop in each column. Note: to move to a new row of knitting when performing C1H, you need to do not 1 (as when performing SC), but 2 VP for lifting. They will be considered the first St in the new row.
To knit a sample, you need to dial a chain of 20 VP, make 2 more lifting VP and then:
- Place the working thread on the hook.

- Insert the tool into the 3rd P of the row (skip 2 VP, they are considered the first column).
- Grab the working thread and pull it through the chain loop from VP.

- Again, grab the working thread and pull it through the pulled out loop and yarn over (2 P will remain on the hook).

- Catch the thread and knit the last 2 P St.

The same method is used to knit columns with 2, 3 or more yarns. First, the required number of yarns is made on the hook, then all the loops are knitted 2 together until they become 1 last one.
Convex and concave columns
Convex and concave columns are also called “under the arch” and “above the arch”. They can be with or without a yarn over, although in the second case they are more difficult to perform due to the high density of the fabric. Externally, the crochet technique resembles an elastic band that is knitted on knitting needles.
If you look at a double crochet, you can see a clear leg with a loop on top:

In regular knitting, the hook is inserted into the loop from above, while in knitting "under the arch" or "over the arch", the tool is inserted under or above the column. This technique allows you to get a stretchy fabric. Usually, convex and concave columns are used for knitting sleeves, narrow necklines, and the bottom edge of outerwear.
Half double crochet
The half double crochet (HDC) is also called strong, since when it is done, the fabric is tight and the loops are voluminous. It is knitted using a similar pattern to double crochets, only in this case the yarn is knitted not separately, but immediately with the main loop.
Attention! To move to a new row when knitting with half double crochets, perform 2 lifting VP.
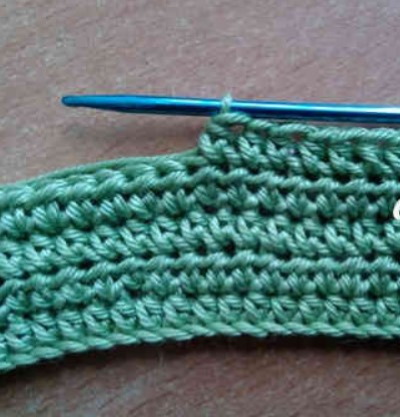

Execution algorithm:
- Make a chain of the required number of VP + 2 VP for lifting.
- Yarn over the hook from above.
- Insert hook into 3 sts from the beginning of the row.
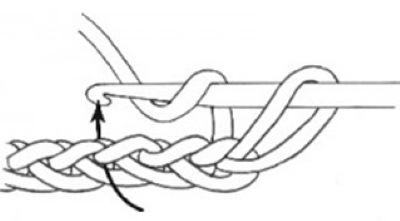
- Grab the working thread and pull it through the loop.

- Grab the working yarn and thread it through all 3 sts on the hook.
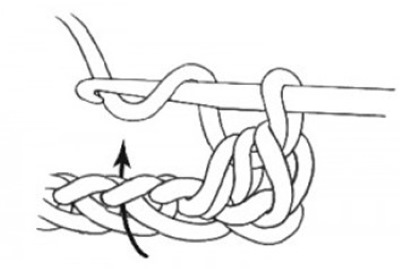
- Next, knit St to the end of the row in the same way.
Unfinished double crochet stitches
Unfinished double crochets are made almost the same way as simple double crochets. The number of yarns can be any (the more, the more voluminous the fabric will be). They are shown on the diagrams by a perpendicular strikethrough on the loop.

Knitting instructions:
- A yarn over is made onto the hook.
- Insert the tool into the next row loop, grab the working thread and pull it through the loop. There are 3 P on the hook: the main one, the yarn over and the one pulled through the loop.
- Knit 2 P (yarn over) together, leaving 2 P on the hook.
- Next, make a yarn over on the hook and insert it again into the next loop of the previous row. The thread is grabbed and pulled out.
- Knit the last 2 loops on the hook together.
- Grab the working thread and knit all 3 sts together.
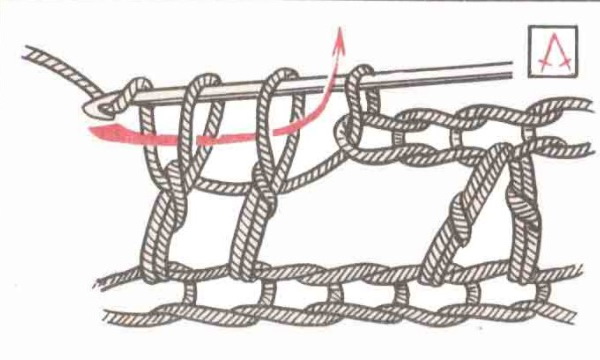
The result is a pattern of 2 НС1Н. According to the same pattern, 3 or more loops are knitted in this way. Note: This method is suitable for reducing stitches in a row. To do this, you do not need to decrease more than 2 stitches at a time, as the fabric will shrink and the decrease will be too noticeable.
Lush column with, without nakida
A lush column differs from an unfinished one only in that the hook is inserted not into each subsequent loop, but into the same one, knitting the required number of columns for the lushness of the pattern. Such a column does not tighten the fabric, does not affect the number of loops in a row.

Execution algorithm:
- Insert the hook into the loop, grab the working thread and pull it out, making the loop high.
- Insert the hook into the same loop of the previous row, grab the thread again and pull it up to the same height as the first.
- Similarly, pull out 2-4 more threads.
- Knit all loops on the hook together.
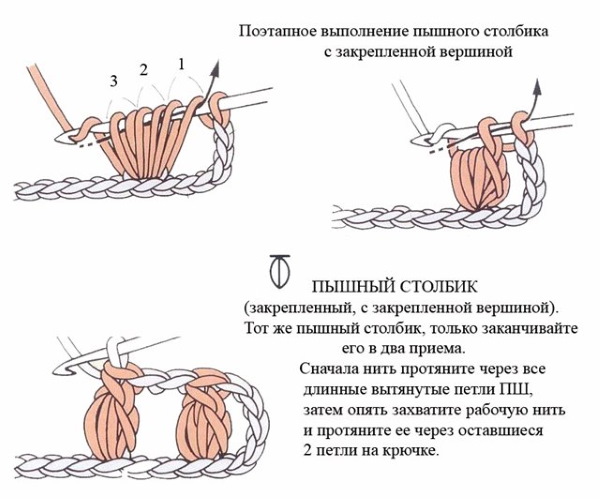
The more columns in one loop, the more voluminous the knitting will be. This pattern is suitable for decorating things and interior items. Warm knitted clothes are usually not decorated with such elements, since the fabric loses density due to large gaps between the loops.
Practicing the skills of knitting single and double crochets on simple items
The double crochet and the single crochet are equally easy to do, but they look different. From the simplest loops, you can knit things that will look stylish and unique.
When knitting in the round, you can use a combination of yarn overs and single crochet stitches in the following items:
- bags;

- laundry baskets;
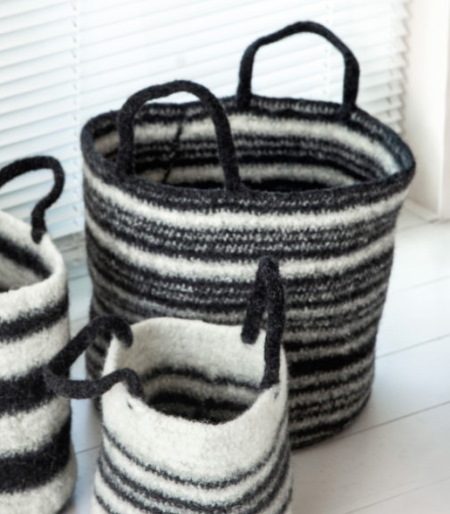

- covers for flowerpots and planters;

- covers for floor lamps and other things.
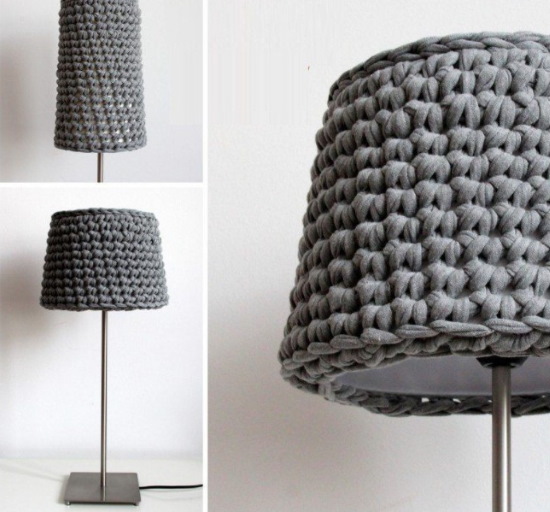

The double crochet and the single crochet can be done in different variations, which will determine the appearance of the fabric. When working with turning rows, the basic knitting elements serve as the basis for creating any patterns.
Rotary knitting of columns allows you to create almost any clothing, interior and decorative items:
- hats and scarves, cardigans, sweaters, vests, skirts, pants;
- bedside rugs and hallway rugs;
- coasters for dining table;
- bedspreads and blankets.
Tips for beginners:
- When crocheting, you need to monitor the tension of the thread: it should always be the same, otherwise the fabric will have uneven elasticity, deform, and stretch excessively.
- The optimal hook size always corresponds to the thickness of the yarn. It is permissible to take a tool 0.25 or 0.5 mm thicker than the yarn, but even then the knitted fabric will be with gaps between the loops.
- To create clothes, you need to take natural yarn. An admixture of synthetics up to 40% is allowed, which allows the finished product to retain its appearance after washing.
- For knitting decorative items, it is better to use synthetic yarn. It does not deform after washing and does not fluff.
Columns with and without yarn overs are basic elements in crocheting. They serve as the basis for any patterns, even openwork ones. When changing the method or side of the thread grip, the appearance of the columns being performed also changes. In this regard, you can use different techniques for their execution when working with one product to decorate or dilute the fabric with unique elements.
Video about knitting
Double crochet and single crochet:
