The fragile beauty of compositions of fresh flowers is short-lived: a few days will pass, and time will begin its destructive work. Only magic or a simple procedure of stabilizing plants can stop the process of withering, which does not require knowledge of magic spells or complex equipment.
What are stabilized plants?
Stabilization (preservation, embalming) of plants and flowers is the process of replacing their natural juices, which nourished the tissues, with an embalming composition. It gradually penetrates all cells, stopping wilting and allowing flowers to retain their attractiveness for a long time.
Compared to live, dried flowers, or artificial dummies, stabilized plants have the following advantages:
- natural appearance: a bouquet stabilized according to all the rules looks the same as its fresh counterpart;
- texture preservation: leaves, stems and buds are indistinguishable from live flowers to the touch;

- no need for careful care: flowers treated with an embalming composition do not need watering, sunlight, and will not become victims of pests and diseases;
- unique strength and elasticity;
- all-season;
- ease of transportation;
- storage periods that are measured not in days, but in years;
- ecological cleanliness;
- maintainability.
Due to their unique qualities, stabilized plants are used today for:
- creation of wedding bouquets;
- ikebana formations;
- creation of flower paintings;
- decoration of premises;
- window dressing.
Such plants are strong, durable, possessing natural beauty, and easily cope with all these tasks.
Plant stabilization technology and the history of its origin
The stabilization method known as glycerinization, widely used in modern industry, was developed in the 1970s by Paul and Jeannette Lambert, a married couple from Belgium who later founded a company called Vermont Florist's House.
Today, professional floristic companies, regardless of their location, can use in their work the following stabilization methods:
- Placing cut plants in embalming solution, which contains substances that freely penetrate all tissues and replace natural fluids.
Then the natural color needs to be restored, for which purpose painting is performed. After processing, the plants regain their former flexibility, plasticity and natural appearance.

- Watering living growing flowers with embalming solution instead of water. An adult flower does not require additional processing, does not change its appearance for a long time, maintaining freshness and brightness of color.
To obtain the source material, crops with dense stems, large buds and leaves are specially grown. The plants are stabilized using the 1st or 2nd method, followed by treatment with compounds that give the necessary strength, restore the natural color and smell.
The resulting specimens are no different from living flowers and are able to remain fresh for 5-10 years.
Methods of stabilization at home
Industrial stabilization methods are quite complex, require a long time, large areas and involve the use of expensive equipment. For amateur florists who want to create their own "eternal" bouquet, there are simple home methods that are simplified versions of industrial technologies.
Preparing inventory
Preserved flowers are long-lived plants that you can create yourself. For this, you will need beautiful specimens that have reached the peak of their attractiveness, without signs of damage or wilting.
Any flowers or their fragments (buds, leaves) are suitable for the procedure. However, plants with dense elastic stems are considered the best. They must be carefully cut, cleaned from dust and slightly dried to remove excess moisture.
You should not delay the drying process: this can lead to a loss of elasticity and a change in the appearance of the plant.
In addition to flowers, the master will need:
- a clean container. Its dimensions depend on the size and quantity of flowers, as well as the chosen method of embalming;
- stabilizing agent (glycerin, paraffin);
- drinking water with low alkalinity;
- sharp knife.

Further actions depend on the stabilization method.
Water and glycerin (1:1)
Glycerin is an alcohol, has a viscous consistency and has the ability to replace the liquid in plant cells (cell sap). This property, as well as the ability of cut flowers to absorb and evaporate moisture, make possible the stabilization process developed by the Lamberts.
In the version suitable for home use, it consists of the following steps:
- Glycerin is mixed with water in equal parts.
- The resulting solution is poured into a container.
- The flower stems are cut to 1 cm (preferably at an angle to increase the suction area).
- While the cut is fresh, the stems are immersed in a container.
- The container is placed in a place out of direct sunlight with humidity of about 40% for about 14 days.

Further actions are reduced to daily cutting of the stem by about 5 mm and adding a glycerin solution: the moisture will gradually evaporate, and the glycerin will replace it.
The fact that the stabilization process is complete is indicated by the high flexibility of the stem and the appearance of small shiny oily drops of glycerin on the tips of the leaves.
Water and glycerin (2:1)
You can change the previous technology by following the following scheme:
- Water is heated to boiling point and mixed with glycerin in a 2:1 ratio;
- The solution is cooled to 70O WITH.
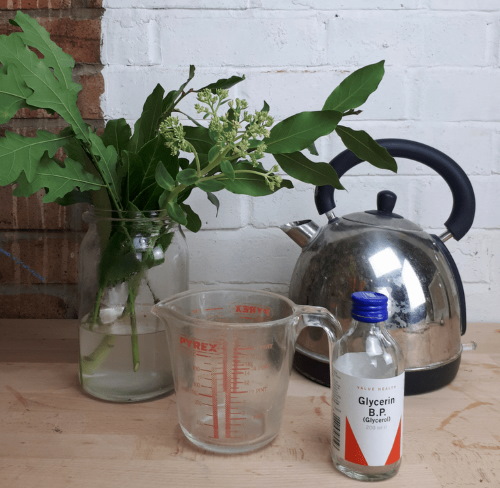

- The flowers are completely placed in a glass container and filled with hot solution.
- After cooling, they are kept in the solution for 15-20 days (depending on the thickness of the stems). All this time, the container should be in partial shade, humidity - about 40%.
- It is necessary to control the level of glycerin and add it as needed. Sometimes they do it easier: every 3-4 days they simply drain the old solution and replace it with a new one.
- After the stabilization process is complete (the flower stems will become more elastic), the plants are removed from the solution and dried.

The main disadvantage of the glycerinization method is the fact that glycerin and the plants obtained with its help are explosive. For this reason, stabilized flowers should not be placed near an open flame: one spark is enough to cause an explosion.
Paraffin
Preserved flowers are flowers that preserve their life for a long period. Wax was used as an embalming agent long before glycerin, in the ancient world.
It is not used in modern industry, but for impatient florists who want to get a flower that will not fade, paraffin (wax) stabilization is the best option. Plants with thick stems and large flowers are suitable for this method.


In addition to these, you will need:
- paraffin (you can use cosmetic or candle wax);
- container or syringe.
The first method involves using a container in which the flower fits completely, and consists of the following steps:
- Paraffin is melted in a water bath and poured into a container in liquid form.
- When the paraffin has cooled slightly (after about 5 minutes), you need to slowly dip the flower into it for a few seconds. Then, to avoid deformation of the petals, the plant is turned with the inflorescence upward.
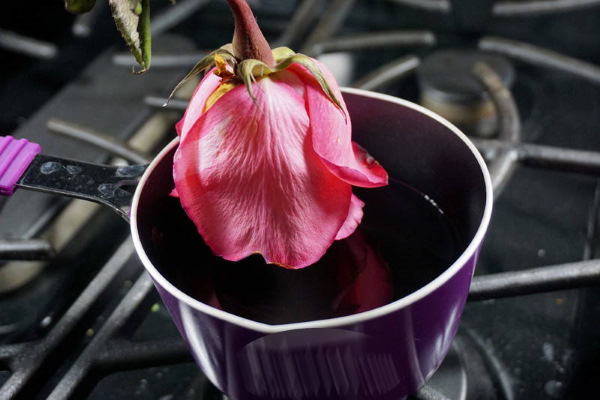
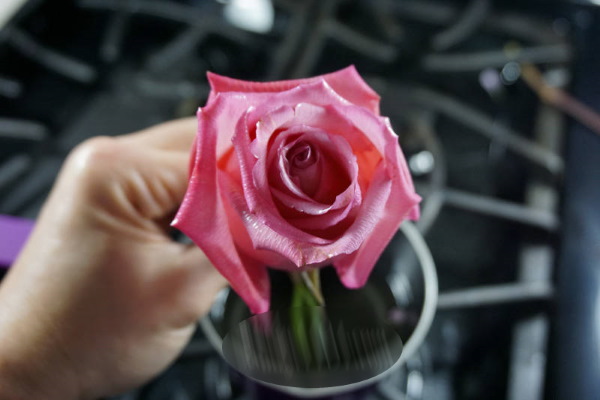


- After the wax layer on its surface hardens (this will take no more than 2 minutes), the procedure is repeated again, and so on 3-4 times, until each of the petals is covered with a thin layer of paraffin.
- To remove excess paraffin, the plant is hung upside down until completely dry.
The 2nd method is suitable only for plants with hollow stems: the wax is heated and in liquid form is drawn into a syringe (without a needle), and then injected into the stem of the plant. The injections are repeated several times until the paraffin fills all the tissues.
Wax flowers look natural, are easy to clean from dust, are not flammable, but the presence of a heat source nearby will melt the paraffin, and the bouquet will quickly become unusable. For this reason, it should be kept in a cool place away from direct sunlight.
Hairspray
Using hairspray is one of the most accessible methods of stabilization, but you need to be prepared for the fact that the effect will be short-lived.
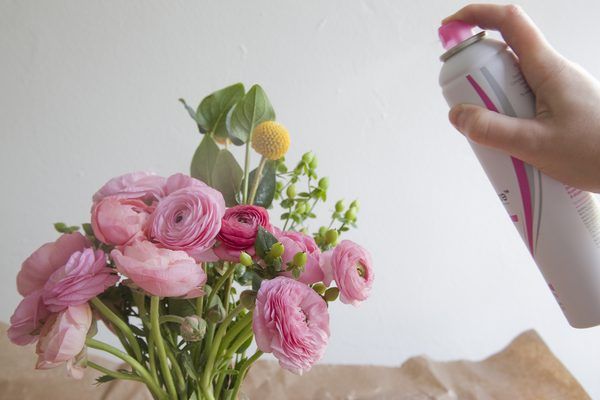

In addition, preserved flowers are fragile and easily break at the slightest touch. To perform the procedure, you need to spray the varnish on the selected flower and wait until it dries.
The disadvantages of the method will be less noticeable if, immediately after processing and drying, you place the plant in a jar with dry sand, silica gel, semolina - any loose substance with high hygroscopicity, and close it tightly.
After about a week, the dehydrator is removed and the flower is treated with varnish again. Next, it is advisable to place it under a glass cap.
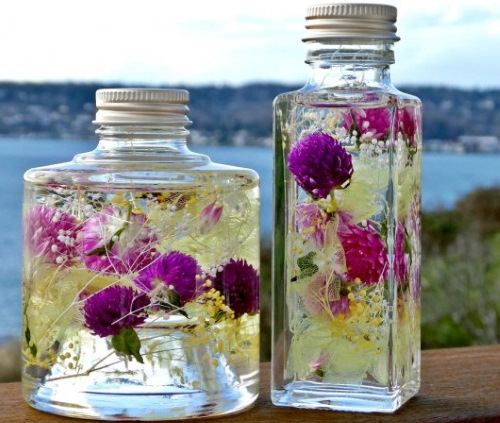
Flowers in a jar
A reliable and simple method of preservation, which does not require even minimal care for stabilized flowers, but its scope of application is limited. Plants processed by this method are used exclusively for interior decoration.
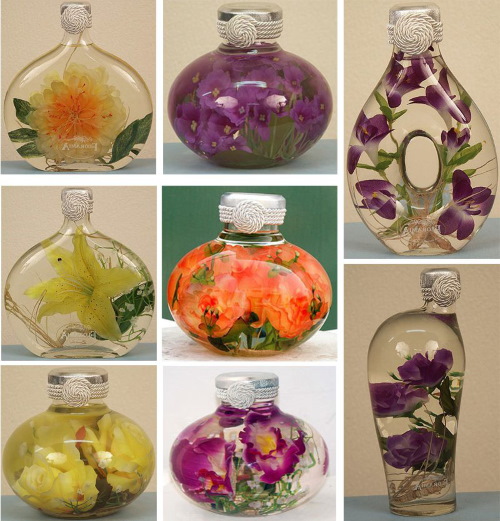

To work you will need:
- flowers and elements that complement the composition: herbs, leaves, moss, shells, beads;
- a beautiful glass container of appropriate volume;
- drinking water;
- glycerol.
The stages of stabilization are as follows:
- A solution is prepared from drinking water and glycerin in a ratio of 2:1.
- Carefully cleaned of dirt and pollen, slightly dried flowers and all other elements of the future composition are placed in a container (nicely and not tightly, but so that they fill the entire volume).
- The flowers are filled with the prepared solution at room temperature. The jar is tightly closed.
- The container is placed in a semi-dark, dry room. While the stabilization process is in progress, it is necessary to control its quantity, promptly adding the solution or replacing it with a new one.
- After about 2 weeks, when the flowers become more elastic and the glycerin does not evaporate, the solution is drained, the contents of the container are washed with water, then a new solution is poured into it, the container is sealed hermetically and, if desired, decorated.
At the final stage, instead of the glycerin solution, you can use a mixture of gelatin and sugar, taken in equal parts, or a strong salt solution.
Giving plants the right shade
Preserved flowers are ordinary living flowers processed in an unusual way. They can be made with a brighter color. For this, food colorings are used, which are added to the embalming solution. This method is suitable for all "glycerin" methods.
An alternative to food colorings will be:
- ink;
- watercolor paints;
- green stuff.
Potassium permanganate is an exception: despite the coloring properties of potassium permanganate, it cannot be used: when entering into a chemical reaction with glycerin, it can cause an explosion.
In order not to ruin your own work with unsuccessful coloring, and to understand how much dye should be used to achieve the desired effect, it is recommended to first experiment on a test sample.
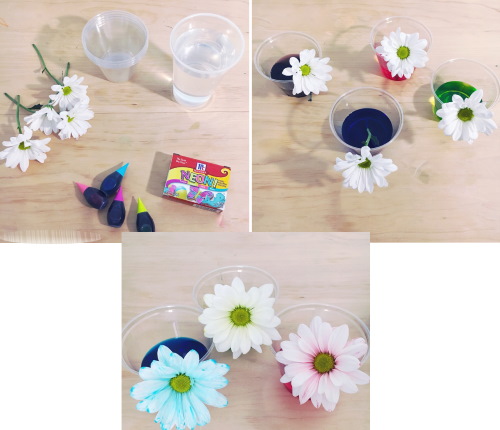

If stabilization is already completed, and the color of the sample for some reason needs to be changed, you can use the second method, which involves coloring the finished samples. Watercolor or acrylic paints are used, which are applied with a thin brush or with a sprayer.
If wax treatment is planned, then color correction must be taken care of at the preparatory stage, by leaving live flowers for several hours in a container with water, to which food coloring of the desired shade has been added.
This method allows you to get flowers of amazing colors. For example, you can split the stem and put its different halves in containers with solutions of different colors: the flower will be two-colored.
Compositions of stabilized flowers
Compositions made from stabilized flowers are durable, unpretentious, environmentally friendly and able to retain a natural appearance. Another important advantage is the ease of their manufacture.
In a flask
Often, to create this souvenir, roses stabilized in any way are used as the source material: varnish, wax, glycerin.
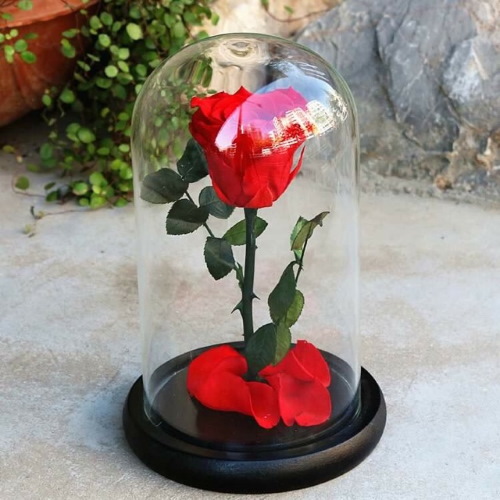

To work you will need:
- flask with wooden base;
- nail;
- awl;
- stabilized rose;
- superglue.
The work is divided into several stages:
- You need to turn the stand over, find its center and hammer in a nail so that it comes out on the back side to a height of about 3 cm.
- If the bud and stem are stabilized separately, then a piece of the stem is cut off from the bud.
- Using an awl, make a hole in the remains of the stem.
- A little glue is poured into the hole.
- The stem is fixed in the hole.
- The nail is treated with glue and the stem is placed on it.
- Petals are glued to the base.
- The composition is closed with a flask.
Pictures from stabilized flowers
Panels created independently from stabilized plants will become an original decoration of the interior, will not require any complex care or protection from pests, will not lose freshness and bright color. A suitable material for a novice master is stabilized moss.
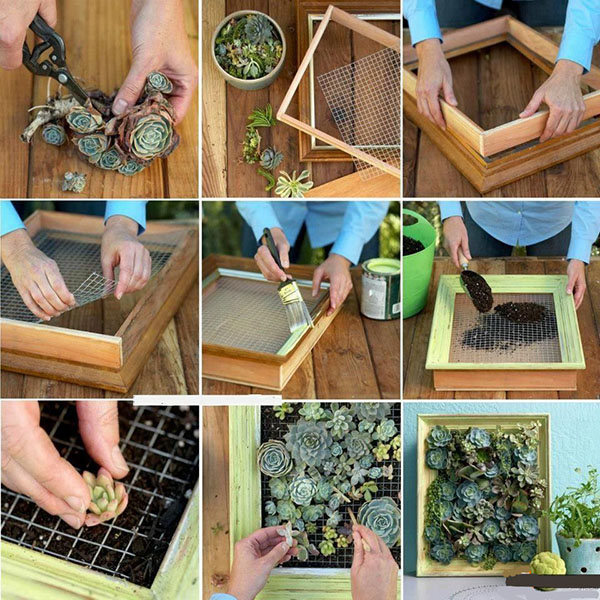

In addition to this, the following is required for work:
- wooden frame;
- glue;
- tassels;
- gloves;
- wood treatment agent.
The stages of work are as follows:
- The edges of the wooden frame are treated with 3 layers of protective compound.
- While the frame is drying, you can trim the ends of the moss to create a flat base and apply glue evenly to the frame.
- It is necessary to tightly place the moss in the frame and wait until the glue dries completely (approximately 5-6 hours).
Wreath
Preserved flowers are long-lived plants that can be used to create wreaths. Such an original accessory will add individuality to the interior and create a festive atmosphere. For example, you can make a simple New Year's wreath from moss, complementing it with appropriate decorative elements.
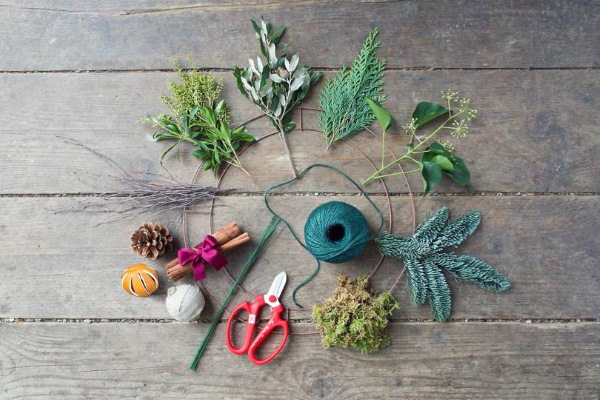
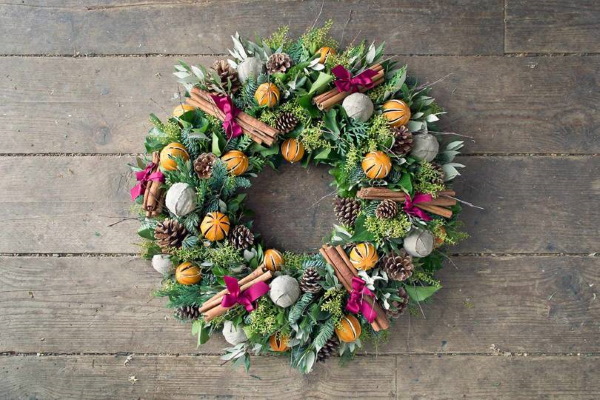



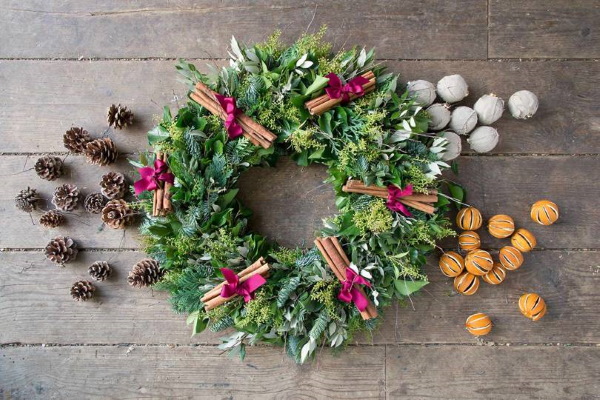

To work you will need:
- moss;
- foam toroidal base;
- PVA glue;
- decor (figurines, cones, balls);
- wire for fastening.
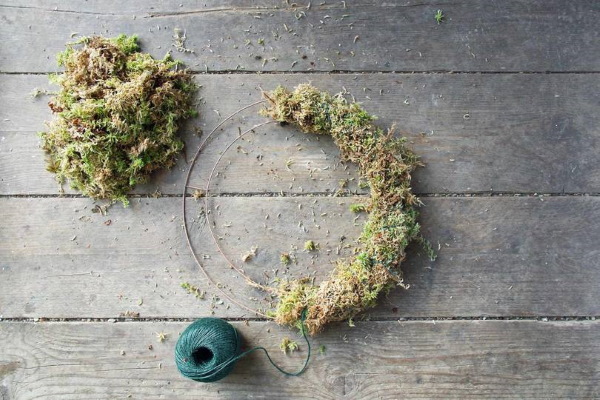
The stages of work are as follows:
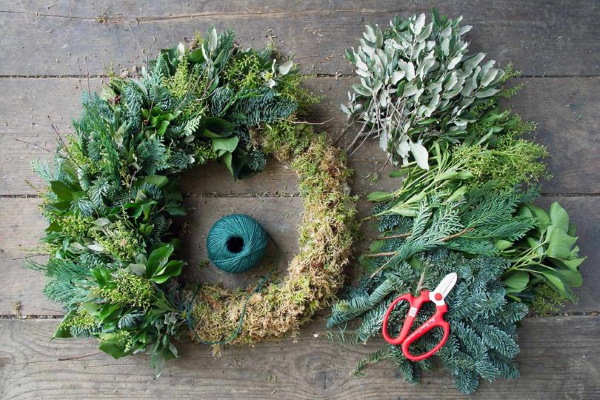
- Glue is applied to the foam base and moss is glued on. It is advisable to process small areas step by step until the entire surface of the wreath is evenly covered with moss.
- Wire is used to attach decorative elements. For example, a deer figurine can be attached using pins, which are glued to the hooves with their rounded ends, and simply inserted into the foam with their sharp ends.
- Similarly, secure other decorative elements, then hang the wreath on the wall using a wide ribbon.
In a pot
Any stabilized plants are suitable for creating a flower arrangement in a vase or pot.
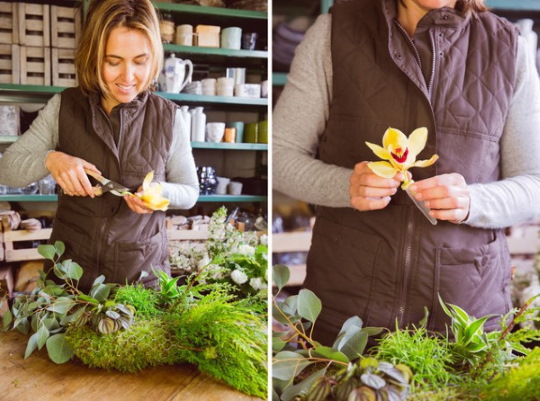



This could be:
- moss;
- eucalyptus leaves;
- roses of different sizes;
- herbs and plants with small flowers.
In addition to these, you will need:
- a pot of appropriate size;
- oasis for artificial flowers (porous material, sponge, base for future composition);
- wire mesh;
- gypsum;
- water.
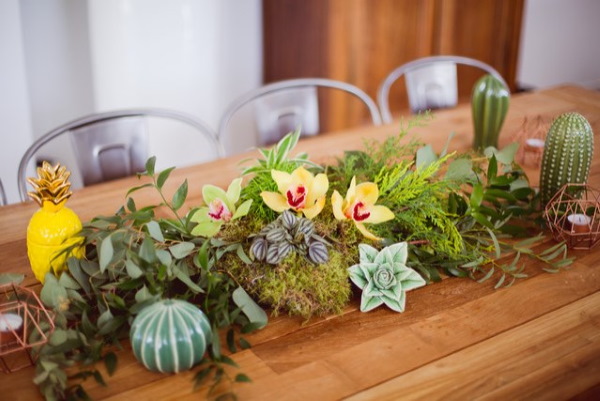

The stages of creation will be as follows:
- Cut the oasis to the desired shape so that it fits freely into the pot.
- Wrap the oasis with wire mesh - it is needed for more secure subsequent fixation of plants.
- Mix the plaster, place the oasis in the pot and fill the spaces between it and the walls of the pot with plaster to secure it securely.
- While the plaster dries, tape the stems of all the elements of the future composition: fix a wire of the required diameter on them (ideally, the same diameter as the stem). The wire is secured with tape.
- Create a base from moss, securing it to the oasis with pins.
- Complete the composition with eucalyptus and stachys leaves, medium-sized roses, and rice flowers.
- Fill the existing “gaps” with any elements in any order, achieving an attractive semicircular shape of the composition.
How to care for preserved flowers
If you provide the stabilized flowers with proper care, the bouquet will remain attractive for a long time.
The rules of care are as follows:
| Aspect | Description |
| Creating optimal conditions | This is maintaining the temperature in the range from 5 to 30 ° C and humidity at 40% (the maximum permissible value is 60%), which practically coincides with the normal parameters for human housing. It is not possible to install a stabilized bouquet:
If transportation is necessary, the plant should be provided with the greatest possible comfort by placing it in a cardboard box with a “paper cushion” (special 2-layer paper with filler) at the bottom. The box is placed on a dry floor or stand. In winter, it is recommended to take the flowers out of the packaging only 2 hours after the box with them is brought into the room. |
| Elimination of negative factors | 
These include:
Short-term exposure to low/high temperatures will not cause much harm to the plant, provided that it is not subjected to such an ordeal too often. |
| Timely cleaning | Unlike synthetic copies, stabilized flowers are not capable of accumulating static electricity, and therefore will not turn into “dust collectors”.
However, dust, which is always present in the air, will inevitably settle on them, giving the bouquet an unkempt appearance and leading to its premature deterioration. Since wet cleaning is out of the question, and wiping with a dry cloth can easily damage the flowers, the only way to remove dust is by blowing. The procedure is performed using a hair dryer set to the "cold" mode. The weakest air flow capable of providing the desired effect is used. If you don’t have a hair dryer, use the softest brushes or combs possible to remove dust. |
Is it possible to extend the "lifespan"
The lifespan of indoor “eternal” flowers is from 2 to 4 years.
It can be extended by:
- strict adherence to the rules described above;
- use of jars and glass flasks;
- timely elimination of minor damage.
As part of the simplest "restoration" work In order to restore the attractive appearance of stabilized plants, you can do the following:
- cutting off damaged leaves or petals - provided that they are small in number, small in size and located in inconspicuous places;
- dividing the flower into fragments (petals), which are then re-fastened together using glue - this method is used when the bud is severely damaged or when using the previous method would disrupt the entire composition;

- removal of the damaged stem surface area by cutting off the top layer (for small sizes);
- removing the stem and replacing it with a leg made of wire wrapped with type tape of the desired color - performed in the case of large-scale damage, when cutting off a layer from the surface is not enough to eliminate the defect;
- coloring of flowers and leaves – required to restore the color of a plant, individual elements of which for one reason or another have lost their brightness. It is done with watercolors or acrylic paints using a small brush or sprayer.
If the damage to the stabilized flowers is too severe, you can create a new composition to replace the one that has become unusable. Thanks to your experience and knowledge, it will be better than the old one.
Video about flowers
Preserved flowers:
